Biochemistry
Our cells engage in protein production, and many of those proteins are enzymes responsible for the chemistry of life.
— Randy Schekman

Fundamental techniques
-
Protein quantification
-
SDS-PAGE (In-gel)
- pre-cast gels (Novex Tris-Glycine Gel, Thermo) [6% | 7.5% | 10% | 12% | 4~15% | 4–20% | 8~16%]
- pre-cast gels (Mini-PROTEIN TGX Gel,BioRad) [8% | 10% | 4~12% | 8~16%]
- Electrophoresis System: [XCell SureLock Mini-Cell, Thermo | Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell, BioRad]
- Reagents: Laemmli Sample buffer, 2-Mercaptoethanol, DTT, Coomassie stain (InstantBlue, Abcam | PageBlue, Thermo)
- Silver Staining: [SilverQuest Silver staining kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific)]: The SilverQuest™ Silver Staining Kit provides a rapid and easy method to silver stain proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Silver staining allows detection of most proteins since it is 30-fold more sensitive than staining with colloidal Coomassie G-250. This kit is specifically designed to provide sensitive silver staining compatible with mass spectrometry analysis. [Original article: Rabilloud et al, 1994]
- SYPRO Ruby Protein Stain: Sypro Ruby is a mass spec compatible protein stain with similar sensitivity as silver stain.
- Instruments: [Amersham™ ImageQuant™ 800, Cytiva | SPARK Plate reader, TECAN]
-
Native-PAGE
- The NativePAGE™ 5% G-250 Sample Additive
- The NativePAGE™ Running Buffer (20X)
- The NativePAGE™ Sample Buffer (4X)
- The NativePAGE™ Cathode Buffer Additive (20X)
-
Western blot
- PVDF membrane, 0.45 um pore size [Millipore: IPFL00010]
- Transfer tank (Wet) [Thermo: VEP-2 | BioRad: | Transfer buffer: CAPS]
- Transfer system (Semi-Dry) [BioRad:]
-
BCA: The BCA (Bicinchoninic Acid) protein assay is a colorimetric method for determining the total protein concentration in a solution. It relies on the reduction of copper(II) to copper(I) by protein in an alkaline solution, followed by the chelation of two molecules of BCA with each Cu(I) ion, resulting in a purple-colored complex that absorbs strongly at 562 nm. The intensity of the purple color is directly proportional to the amount of protein present, allowing for quantification by comparing the absorbance to a standard curve of known protein concentrations.
- Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kits [User guide: PDF | measure at 562 nm]
- Pierce™ Dilution-Free™ Rapid Gold BCA Protein Assay Kit [User guide: PDF | measure at 480 nm]
-
Bradford: The Bradford method is a quick and widely used colorimetric assay for determining protein concentration. It involves the binding of a dye, Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250, to proteins, which causes a shift in the dye’s absorbance spectrum. By measuring the absorbance of the resulting blue solution at 595 nm and comparing it to a standard curve, the protein concentration can be determined. [original article, PMID:942051]
- Calculation of Protein Extinction Coefficients: The molar absorption coefficient of a peptide or protein is related to its tryptophan (W), tyrosine (Y) and cysteine (C) amino acid composition. At 280nm, this value is approximated by the weighted sum of the 280nm molar absorption coefficients of these three constituent amino acids. [Online calculator]
-
ELISA
-
-
Protein purification
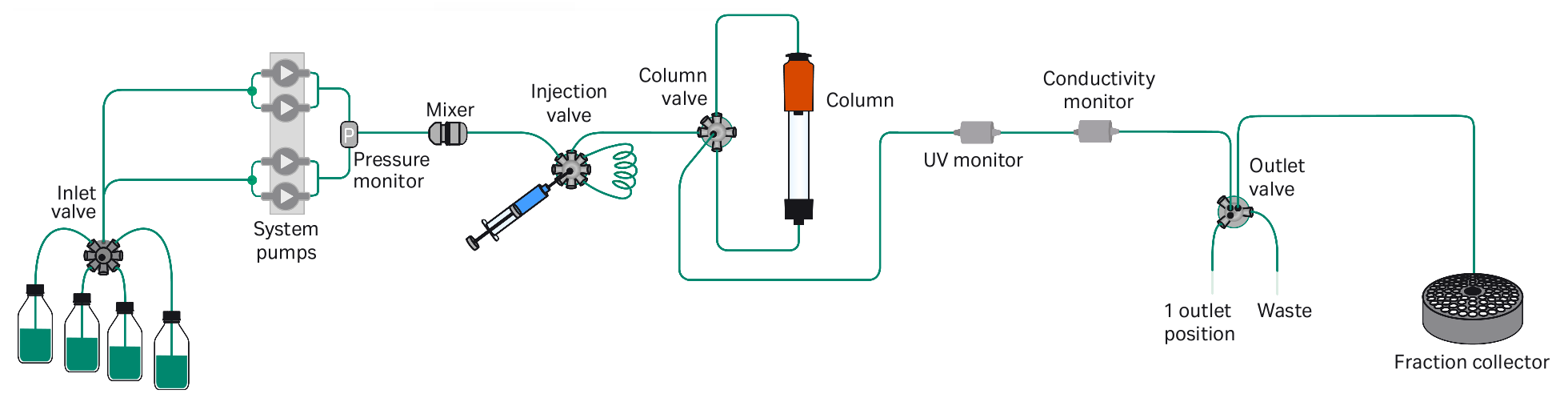
- ATKA Pure [Cytiva | ÄKTA™ Laboratory-scale Chromatography Systems]: ATKA Pure is a modern, compact, flexible and intuitive FPLC (Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography) system for fast purification of proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids from microgram to gram levels of the desired compound. Can be used for affinity chromatography, size exclusion chromatography (SEC, also known as gel filtration), ion exchange chromatography, hydrophobic interaction chromatography, and reversed phase chromatography (RPC). [Equipment SOP, PDF]
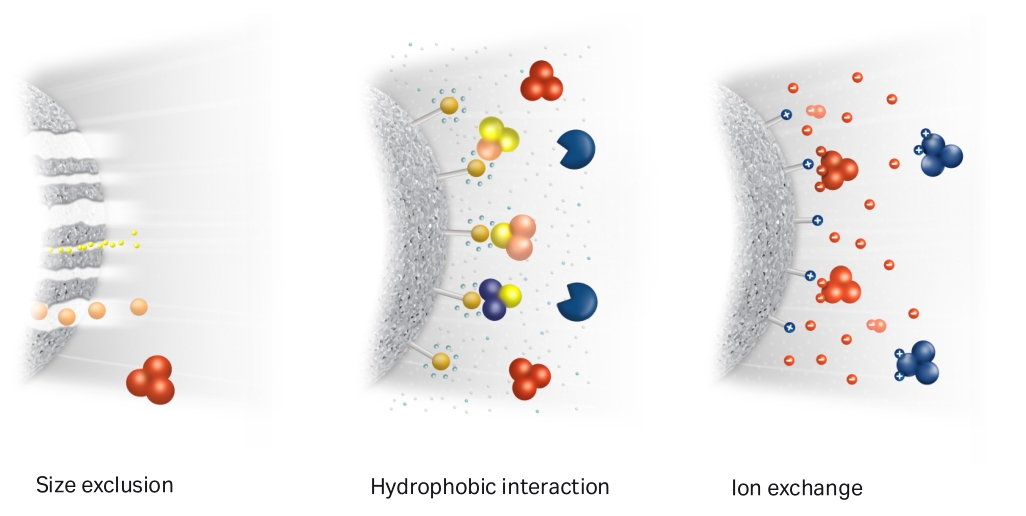
- Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC, Gel filtration): [Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL, Sigma, GE29-0915-96 | Superdex 200 | Superdex 75 | TSKgel G4000SWxl, Tosoh]
- Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC): Phenyl-HP cartridge
- Anion exchange chromatography (AEC): [HiTrap Q, Cytiva, 17115401 | Capto HiRes Q 10/100 | Mono Q 5/50 GL | HiTrap DEAE FF]
- Cation exchange chromatography (CEC): [SP-Sepharose, Cytiva | Capto HiRes S 10/100]
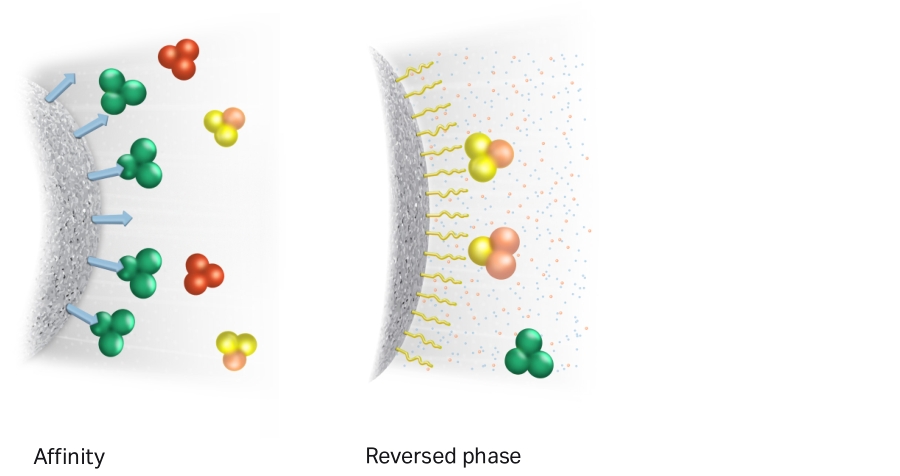
- Affinity chromatography (AC): Heparin-affinity chromatography uses immobilized heparin to purify proteins by exploiting their ability to bind to the highly negatively charged glycosaminoglycan. [HiTrap-Heparin HP]
- Reverse Phase chromatography (RPC): Reverse phase chromatography uses columns packed with a non-polar, hydrophobic resins such as polystyrene/divinyl benzene particles.
- Affinity Tag based purification:
- Anti-FLAG: anti-Flag M2 affinity gel [Millipore Sigma]
- Twin-Strep: The Twin-Strep-tag® (WSHPQFEKGGGSGGGSGG-SAWSHPQFEK) is a tandem version of the Strep-tag®II with an internal linker region. This twin version with the same specificity but higher affinity to Strep-Tactin® enables efficient purification even in batch or directly from culture supernatants.
- His-Tag: [Ni-NTA resin | HisTrap HP]
- GST-Tag: [Selection guide, Cytiva | PMID: 26096507]
- Purifying Challenging Proteins, Principles and Methods [PDF]
- Simulation software: Protein Purification starts off by letting you examine how a simple mixture of proteins behaves during gel filtration and ion-exchange chromatography and then goes on to allow the design and testing of full purification protocols using more complex mixtures of proteins.
- Compute isoelectric point (pl): [ExPASy | Protein isoelectric point calculator]
- ATKA Pure [Cytiva | ÄKTA™ Laboratory-scale Chromatography Systems]: ATKA Pure is a modern, compact, flexible and intuitive FPLC (Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography) system for fast purification of proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids from microgram to gram levels of the desired compound. Can be used for affinity chromatography, size exclusion chromatography (SEC, also known as gel filtration), ion exchange chromatography, hydrophobic interaction chromatography, and reversed phase chromatography (RPC). [Equipment SOP, PDF]
-
Protein interaction
- Non-Covalent Bonds and Interactions: Hydrogen Bonds, Ionic Bonds (Salt Bridges), Van der Waals Interactions, Hydrophobic Interactions
- Covalent Bonds: Disulfide Bonds
- co-IP: Anti-FLAG (DYKDDDDK) Magnetic Agarose beads [Thermo | Sigma]; Anti-HA Magnetic Agarose [Thermo]
- cross linking reagents:
- Magnetic Separation Rack: [DynaMag™-2 Magnet]
- SPR (Surface plasmon resonance): SPR is a phenomenon that occurs where electrons in a thin metal sheet become excited by light that is directed to the sheet with a particular angle of incidence, and then travel parallel to the sheet. Assuming a constant light source wavelength and that the metal sheet is thin, the angle of incidence that triggers SPR is related to the refractive index of the material and even a small change in the refractive index will cause SPR to not be observed. [Biacore T200, Cytiva | ]
- BLI (Bio-layer interferometry): [ForteBio Octet 96e]
-
Protein identification
- Protein sequencing:
- N-terminal sequencing (Edman degradation):Step-by-step N-terminal sequencing, is a classic technique to analyze the N-terminal amino acid sequence of protein or polypeptide by chemical directional cleavage and identification. This technology was initiated by Swedish biochemist Pehr Edman in 1950, and was automated in 1967 (liquid-phase pulse sequencer) [Source]
- De novo sequencing based on MS
- AP-MS: Affinity purification coupled with mass spectrometry (AP-MS) is a widely used approach for the identification of protein-protein interactions.
- the contaminant repository for affinity purification (the CRAPome) [Website]
- Proximity labeling: APEX[]; TurboID[]; UltraID[]
- Protein sequencing:
-
Protein expression system
- E.coli: [BL21(DE3) strain + pET-28a+ vector | Rosetta(DE3) strain]
- Yeast:[S. cerevisiae strain yMLT62 (J. Thorner lab) | yeast strain ySS025 (ref.) | Pichia pastoris expression system]
- Sf21 insect cells: [Bac-to-Bac Baculovirus Expression System (Life technologies) | FastBac | flashBAC]
- Expi293F cells: Expi293F Cells are human cells derived from the 293F cell line, they are maintained in suspension culture and optimized to grow to high density in Expi293 Expression Medium. Expi293F Cells are highly transfectable and generate superior transient protein
yields compared to standard 293 cell lines. [Expi293 Expression Medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific) | Expi293 Expression System User guide, PDF]
- Growth conditions: Suspension at 37℃, 8% CO2.
- ExpiCHO-S cells: The Gibco ExpiCHO Expression System brings together a high-expressing CHO cell line, a chemically-defined animal origin-free, serum-free, and protein-free culture medium, an optimized culture feed, and a high-efficiency transfection reagent that work in concert to provide protein titers 3x higher than the Gibco Expi293 Expression System and 160x higher than the Gibco FreeStyle CHO Expression System. [User Guide, PDF]
We are seeing cells more and more clearly as chemical factories, where the various products are manufactured in separate workshops, the enzymes act[ing] as the overseers.
— Eduard Buchner (The Founder of Modern Biochemistry)
-
Organelle isolation
- mitochondria: Mito-IP []; Mito-IP tg mice
- Lysosome: LysoIP [PMID: 29074583 | Protocol] ; LysoIP tg mice (Rosa26;lox-stop-lox-TMEM192-3×HA) [PMID: 36131016]
- ER: ER-IP
- Golgi: Golgi-IP [PMID: 37155866 | Protocol]
- Synaptosome: [A rapid Percoll gradient procedure, 2008, DOI Link]
- Postsynaptic density (PSD): [DOI Link]
-
Cell culture basis
-
ATCC® ANIMAL CELL CULTURE GUIDE (tips and techniques for continuous cell lines) [PDF]
-
Cell Culture Basics Handbook [PDF]
-
Guideline of Cell biology experiment, Part I (In Chinese, 细胞实验指南(上)) [PDF]
-
Guideline of Cell biology experiment, Part II (In Chinese, 细胞实验指南(下)) [PDF]
-
Gibco Cell Culture Basics Handbook(In Chinese) [PDF]
-
Primary neuron culture
-
Cell lines from ATCC library
Name ATCC Catalog Organism Description HEK293T xxxx Homo sapiens Hela xxxx Homo sapiens SH-SY5Y CRL-2266 Homo sapiens U-2 OS HTB-96 Homo sapiens bEnd.3 [BEND3] CRL-2299 Mus musculus HUVEC Lonza, CC-2519 Homo sapiens THP1 ATCC, TIB-202 Homo sapiens human leukemia monocytic cell line
-
-
Transfection reagents
- XtremeGene9: Sigma
- PEI: PEI MAX 40k (Polysciences)
-
Stable cell line generation
- Lenti-virus system
Vendor companies
- Cell Signaling Technology: We order antibodies in this company.
- Abcam: We order antibodies in this company.
- ThermoFisher
- R&D Systems
- BioRad
- ATCC: ATCC has the world’s largest and most extensive product catalog of human and animal cell lines for research purposes.
- Gibco
- Corning
- HyClone
- Sigma
Ref. Labs
Signaling pathways
-
Discovery of cGAS-cGAMP pathway and its role in immune defense
- Sun, Lijun, et al. “Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway.” Science 339.6121 (2013): 786-791. [PDF | PMID: 23258413 | DOI Link]
- Wu, Jiaxi, et al. “Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA.” Science 339.6121 (2013): 826-830. [PDF | DOI Link]
-
Discovery of MAVS, a Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Adaptor Protein
- Seth, Rashu B., et al. “Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-κB and IRF3.” Cell 122.5 (2005): 669-682. [PDF | PMID: 16125763 | DOI Link]
-
The discovery of mTOR
- Sabatini et al. “RAFT1: a mammalian protein that binds to FKBP12 in a rapamycin-dependent fashion and is homologous to yeast TORs.” Cell 78.1 (1994): 35-43. [PDF | DOI Link]
- iBiology Talk [PartI: Introduction to mTOR and the regulation of growth]
-
Discovery and systematic characterization of basic mechanisms that regulate growth including nutrient sensing pathways
- Nutrient sensors: [CASTOR | Sestrin2 | SAMTOR]
- Nutrient sensing hub: [GATOR1 | GATOR2 | KICSTOR]
- iBiology Talks [PartII: Regulation of mTORC1 by nutrients | PartIII: Ribophagy and nucleotide recycling]
- Xiaodong Wang lab, UTSW; NIBS
- The discovery of mitochondria CytoC mediated apoptosis pathway
- Zou, Hua, et al. “Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c–dependent activation of caspase-3.” Cell 90.3 (1997): 405-413. [PDF | PMID: 9267021 | DOI Link]
- Characterization of TSC2 as upstream negative regulator of mTORC1
- Inoki, Ken, Tianqing Zhu, and Kun-Liang Guan. “TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival.” Cell 115.5 (2003): 577-590. [DOI Link]
- Ronald David Vale lab, University of California; San Francisco/HHMI
-
The discovery of Kinesin [iBiology Talk]
- Vale, Ronald D., et al. “Direct observation of single kinesin molecules moving along microtubules.” Nature 380.6573 (1996): 451-453. [PDF | PMID: 8602245 | DOI Link]
-
The Characterization of Molecular Motor Proteins [iBiology Talk 1 | iBiology Talk 2 | iBiology Talk 3]
- Sablin, Elena P., et al. “Crystal structure of the motor domain of the kinesin-related motor ncd.” Nature 380.6574 (1996): 555-559. [PDF | PMID: 8606780 | DOI Link]
- Vishva Dixit lab, Genentech
-
Summary of all research and key publications [PDF]
-
Define a death receptor-induced apoptotic pathway
-
Tewari, Muneesh, and Vishva M. Dixit. “Fas-and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the poxvirus crmA gene product.” Journal of Biological Chemistry 270.7 (1995): 3255-3260.
-
key downstream executioner protease: YAMA/caspase-3
- Tewari, Muneesh, et al. “Yama/CPP32β, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase.” Cell 81.5 (1995): 801-809.
-
FADD-caspase-8 pathway as the central apoptotic conduit used by all death receptors: [FADD | FLICE/caspase-8]
- Pan, Guohua, et al. “The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL.” Science 276.5309 (1997): 111-113. [PMID: 9082980]
-
-
The discovery and characterization of non-canonical Inflammasome pathway that responds to the presence of intracellular LPS independent of toll-like receptors
- Kayagaki, Nobuhiko, et al. “Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11.” Nature 479.7371 (2011): 117-121. [PMID:22002608]
- Kayagaki, Nobuhiko, et al. “Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling.” Nature 526.7575 (2015): 666-671. [PMID:26375259]
-
The first to show that RNAi could be the basis for therapy in an animal model
-
Identification of novel mechanisms of mitochondrial and DNA damage activated by granzyme A
- The discovery and characterization of GSDMD mediated pyroptosis pathway [Online Talk]
- The discovery and characterization of Nucleic acid sensors
- Discoveries concerning the DNA-damage response — a fundamental mechanism that protects the genomes of all living organisms
Transcriptional regulation and epigenetics
- The discovery of the SV40 large T antigen
- Tjian, Robert. “The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein.” Cell 13.1 (1978): 165-179. [PMID: 202398 | DOI Link]
- The discovery of first histone demethylase, LSD1
- The discovery of first RNA demethylase that oxidatively reverses N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation in mammalian messenger RNA
Ref. softwares
- PyMOL: PyMOL is a user-sponsored molecular visualization system on an open-source foundation, maintained and distributed by Schrödinger.
- UCSF ChimeraX: UCSF ChimeraX (or simply ChimeraX) is the next-generation molecular visualization program from the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics (RBVI), following UCSF Chimera.
- HMMER: HMMER is a software package that provides tools for making
probabilistic models of protein and DNA sequence domain families –
called profile hidden Markov models, profile HMMs, or just profiles
– and for using these profiles to annotate new sequences, to search
sequence databases for additional homologs, and to make deep multiple sequence alignments.
- HMMER underlies several comprehensive collections of alignments and profiles of known protein and DNA sequence domain families, including the Pfam database. [User’s Guide]
- Pfam 35.0
- The Pfam database is a large collection of protein families, each represented by multiple sequence alignments and hidden Markov models (HMMs).
- Pfam 35.0 contains a total of 19,632 families and clans.
- Proteome-pI: Database of pre-computed isoelectric points for proteomes from different model organisms (5029 species).
Tool development
- PROXIMITY LABELING
- APEX
- TurboID
- LOV-Turbo: Light-regulated TurboID
- Stanford Neuro-omics Initiative, 2020 Virtual Workshop
- “Proteomics and proximity labeling in neuroscience”, by Alice Ting [YouTube video | Slides]
- “Design and execution of proximity labeling experiments”, by Tess Branon [YouTube video | Slides]
- “Analysis of proximity labeling data”, by Shuo Han [YouTube video | Slides]
Ref. Protocols
Nobel laureates
- Carolyn Bertozzi, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA; Howard Hughes Medical Institute, USA [lab link]
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2022
The Bioorthogonal Chemistry Journey, from Laboratory to Life [Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source]- iBiology Talk[PartII: Imaging the glycome]
-
Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom; Francis Crick Institute, London, United Kingdom
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019
Elucidation of Oxygen Sensing Mechanisms in Human and Animal Cells [Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source] -
William G. Kaelin Jr, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA; Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Chevy Chase, MD, USA; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA; Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, USA The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019
The von Hippel-Lindau Tumor Suppressor Gene: Insights into Oxygen Sensing and Cancer [Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source] -
Gregg L. Semenza, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019
Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Physiology and Medicine [Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source]
-
James P. Allison, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy [Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source] -
Tasuku Honjo, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018
Serendipities of Acquired Immunity [Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source]
- James E. Rothman, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2013
The Principle of Membrane Fusion in the Cell [Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source]
- Thomas A. Steitz, Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA/HHMI
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009
From the Structure and Function of the Ribosome to New Antibiotics [[Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source]
- Roger D. Kornberg (1947-), Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2006
The Molecular Basis of Eukaryotic Transcription [[Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source]
-
Aaron Ciechanover (1947-), Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004
Intracellular Protein Degradation: From a Vague Idea thru the Lysosome and the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and onto Human Diseases and Drug Targeting [[Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source] -
Avram Hershko (1937-), Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004
The Ubiquitin System for Protein Degradation and some of its Roles in the Control of the Cell Division Cycle [[Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source] -
Irwin Rose (1926-2015), University of California, Irvine, CA, USA
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004
Ubiquitin at Fox Chase [[Nobel Lecture video | Lecture Slides | Read the Lecture | Source]
-
H. Robert Horvitz, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, MA, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2002
Worms, Life and Death [[Nobel Lecture video | Read the Lecture | Source] -
John E. Sulston, The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2002
C. elegans: The Cell Lineage and Beyond [[Nobel Lecture video | Read the Lecture | Source] -
Tim Hunt, Imperial Cancer Research Fund, London, United Kingdom
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2001
Protein Synthesis, Proteolysis, and Cell Cycle Transitions [Nobel Lecture video | Read the Lecture | Source | Careers interview] -
Günter Blobel (1936-2018), Rockefeller University, New York, NY, USA/HHMI
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1999
Protein Targeting [Nobel Lecture video | Read the Lecture | Source] -
Jens C. Skou (1918-2018), Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1997
The Identification of the Sodium-Potassium Pump [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Michael S. Brown, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, TX, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1985
A Receptor-Mediated Pathway for Cholesterol Homeostasis [Nobel Lecture video | Read the Lecture | Source] -
Joseph L. Goldstein, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, TX, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1985
A Receptor-Mediated Pathway for Cholesterol Homeostasis [Nobel Lecture video | Read the Lecture | Source] -
David Baltimore (1938-2025), Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, MA, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1975
Viruses, Polymerases and Cancer [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Christian de Duve (1917-2013), Rockefeller University, New York, NY, USA, Université Catholique de Louvain, Louvain, Belgium
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1974
Exploring Cells with a Centrifuge [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Arthur Kornberg (1918-2007), Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959
The Biologic Synthesis of Deoxyribonucleic Acid [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Severo Ochoa (1905-1993), New York University, College of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1959
Enzymatic Synthesis of Ribonucleic Acid [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Hans Adolf Krebs (1900-1981), Sheffield University, Sheffield, United Kingdom
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1953
The Citric Acid Cycle [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Fritz Albert Lipmann (1899-1986), Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1953
Development of the Acetylation Problem: A Personal Account [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Otto Heinrich Warburg (1883-1970), Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut (now Max-Planck-Institut) für Biologie, Berlin-Dahlem, Germany
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1931
The Oxygen-Transferring Ferment of Respiration [Read the Lecture | Source] -
Eduard Buchner (1860-1917), Landwirtschaftliche Hochschule (Agricultural College), Berlin, Germany
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1907
for his biochemical researches and his discovery of cell-free fermentation [Read the Lecture | Source]
We must never let ourselves fall into thinking “ignorabimus” (“We shall never know”), but must have every confidence that the day will dawn when even those processes of life which are still a puzzle today will cease to be inaccessible to us natural scientists.
— Eduard Buchner (December 11, 1907)